College and Career Planning
Mining involves much more than just digging minerals out of the ground. In order to effectively plan and run a mine, companies must work with experts in many different fields including health, science, engineering, environment, social science, business and law. See the descriptions below for just a few of the technical paths you can pursue for a career in the mining industry.
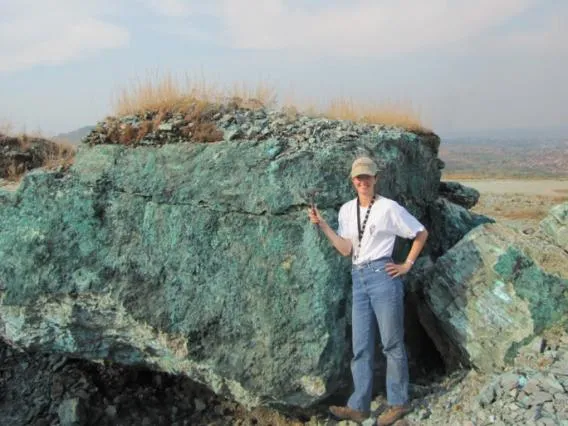

Geologists
Geologists are scientists who understand the rocks, minerals and structures that make up the earth. They play a major role during exploration (finding and characterizing ore deposits), mine planning, mine operations and reclamation of closed mines. Other specialized career fields in geology applied to mining include geophysicists, geochemists and hydrogeologists.
Why should I become a Geologist?
How do I become a geologist?
Most mining geologists have a BS in geology, geoscience or earth science. Many also obtain an MS and PhD. The entry-level degree for many jobs in mining is an MS.
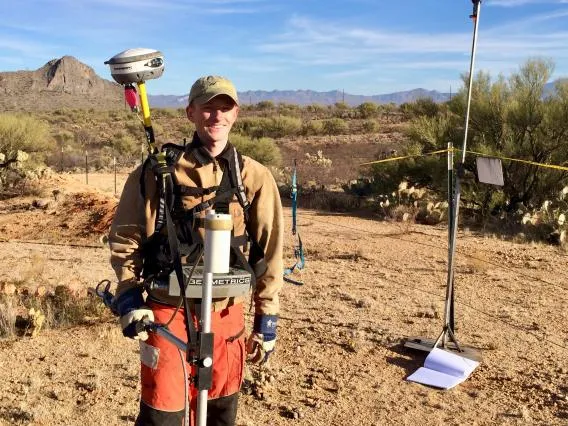

Mining Engineers
Mining engineers understand the entire mining process including the business and management aspects of mining. They use this integrated understanding to design the mine, choose the best equipment and best practices for excavating and processing. Some engineers specialize in ventilation (regulating the temperature and air quality in underground mines), mine automation and technology (how to manage the Terabytes of data generated from all the machines and how to use autonomous vehicles), and how to finance mines (the business of mining).
Why should I become a Mining Engineer?
How do I become a mining engineer?
Most mining engineers have a BS in geological engineering. Some also get an MS, ME or PhD.
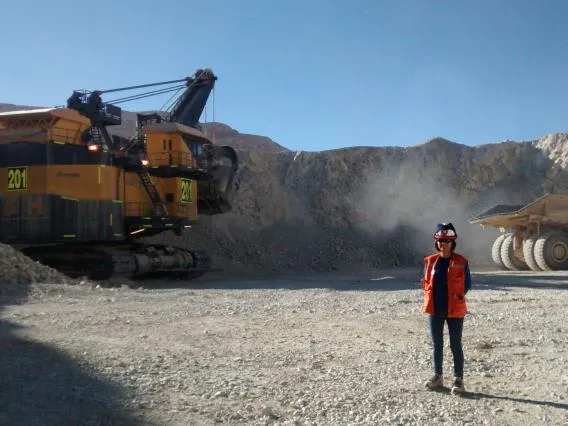

Mineral Processing Engineers
Mineral Processing engineers specialize in mineral processing (determining how to separate valuable material from waste rock) and extractive metallurgy (extracting elements from minerals). They apply their expertise in the chemistry of minerals to separate the economic from uneconomic minerals and to separate the elements in each mineral. They also play an important role in managing water quality at the mine site, the energy usage and environmental footprint of mines during and after mining.
Why should I become a Mineral Processing Engineer?
How do I become a Mineral Processing Engineer?
Most mineral processing engineers have a Bachelor of Science (BS) in mining engineering, extractive metallurgy, mineral engineering or chemical engineering. Some also get an MS, ME or PhD.
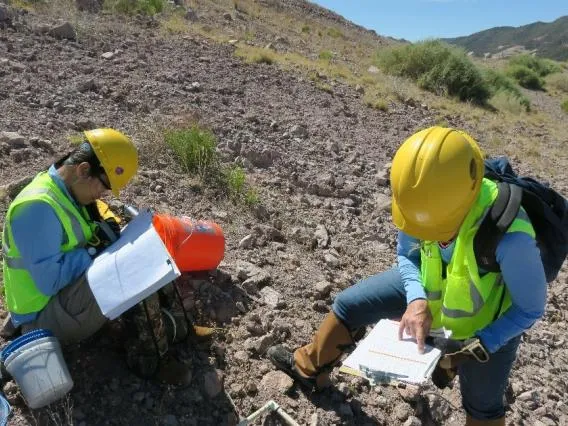

Environmental Engineers and Scientists
Environmental engineers and scientists must design, build and operate systems that monitor water quality, mitigate dust and other hazards and restore land disturbed by mining activity. Many specialists are needed to ensure safe environmental conditions during and after mining, including hydrologists, biologists, ecologists, chemists, chemical engineers and even electronics engineers.
How do I become an environmental specialist?
Environmental scientists have a BS, MS or PhD in a field such as environmental science, ecology, hydrology or geology. Environmental engineers often have a degree in environmental or chemical engineering.

Health and Safety Specialists
Health and Safety Specialists are responsible for keeping workers safe and healthy on the job. They design equipment and protocols that protect everyone on the job site. Some safety specialists include industrial hygienists (experts in preventing industry related illnesses), Occupational Health and Safety Specialists (experts in the laws and regulations related to safety on the mine site), and Safety Engineers (people who help design safety features of systems and equipment).
How do I become a safety specialist?
Many safety specialists start with a BS in Public Health and some continue on to get a MPH (Master of Public Health).

Data Scientists
Data scientists are responsible for handling, processing and interpreting huge data sets in real time. Modern mining means 24-hour, real-time analysis and interpretation of everything from huge autonomous haul trucks to drills to slope movement, water flow rates and water quality. These advancements are only useful if we have advanced computing power as well as experts to design and understand these systems.
How do I become a data analytics engineer?
Experts are needed in many fields relating to big data
UA COMPUTER AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Interactive Map: UArizona alumni's Global Careers
From Indonesia to Alaska, explore our interactive global map and see where University of Arizona alumni and students have been and the exciting things they've done!
Discover a range of companies and roles within mining and mineral resources for many disciplines.

'Ask a Pro' interview series
What does a Mining Engineer do? What do you love about your job? What advice do you have for high school students? The 'Ask A Pro' career-exploration video series gives you a chance to explore your interests and career options by connecting with industry professionals. Through these short interview videos students can hear professionals' real world experiences!

